Deep learning segmentation & measure of traits
For roots or aerial parts
Image
Deep learning
Python
Abstract
This tool enables fast, deep learning (Reinforcement Learning) segmentation of high-resolution images. The script then performs measurements such as projected area, shape width and height, perimeter, skeleton…
Background
This script has been used and published in OCL journal in 2021. Please quote this source if you use this script.
Graphical overview
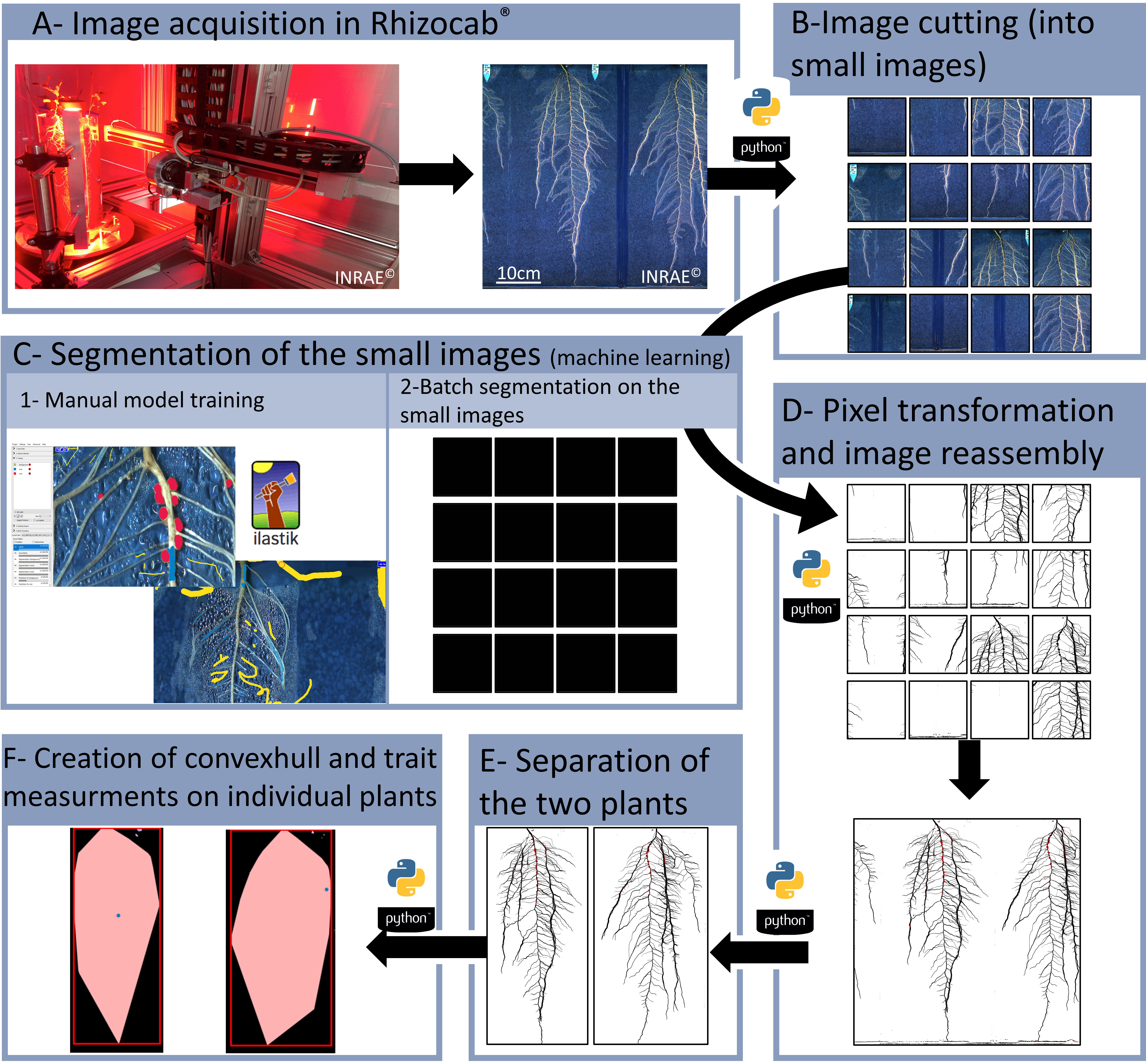
Flow chart representing the different steps of root trait analysis.
- High-throughput phenotyping on the 4PMI platform; true color high resolution image (12 000 x 12 000 pixels) of soybean roots.
- Cutting of the large image into small images.
- Segmentation by using ilastik
- Learning at different positions on the images obtained from several RhizoTubes®. Creation of a predictive model. Adjustment of the model by correcting segmentation errors.
- Use of the model on all the small images. After segmentation, each pixel of the image was worth the value 0, 1 or 2 and corresponded respectively to the background, the roots or the nodules (black image).
- Image conversion into white, black and red images (respectively the background, the roots and the nodules). These segmented images were then reassembled.
- The two plants were extracted from the image to be analyzed individually.
- The root projected area, nodule projected area were then measured as well as the width, depth, area and perimeter of the convex hull. Once the template is created it takes approximately 14 minutes from C2 to F.
Article Information
How to cite
Readers should cite the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Maslard C, Arkoun M, Salon C, Prudent M (2021) Root architecture characterization in relation to biomass allocation and biological nitrogen fixation in a collection of European soybean genotypes. OCL 28: 48. doi: 10.1051/ocl/2021033